Non statutory non qualified stock option plan
Please contact customerservices lexology. This is a frequently asked question as many U. This post will provide a general summary of the tax consequences both to the recipient of an ISO or NSO and to the issuing company.
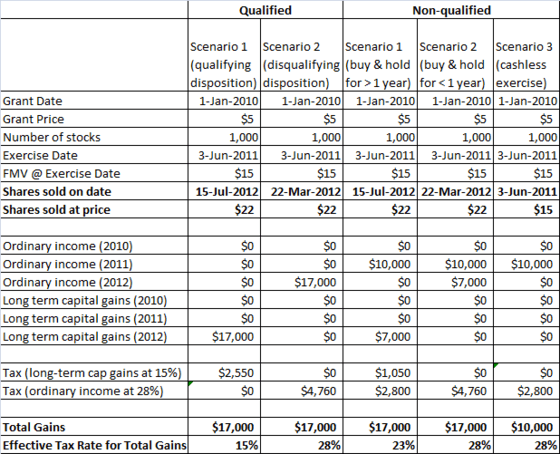
Subject to certain exceptions as discussed below, an ISO is generally eligible for the following tax benefits: The employee is eligible for these advantageous tax consequences only if the employee does not dispose of the shares received pursuant to the exercise of the ISO within 2 years from the date of the granting of the ISO nor within 1 year after the ISO was exercised.
We note that in practice, ISOs are generally only granted by public companies where liquidity could be obtained by the recipient prior to a sale of the company and therefore the required share holding period of 1 year after exercise can be satisfied.
Qualified vs Non-qualified Stock Options - Difference and Comparison | Diffen
In addition, the employee must exercise the ISO within three months after ceasing to be employed by the company or its subsidiary or parent or one year in the case of cessation of employment caused by permanent disability. Here is a summary describing this hypothetical, using the date of issuance as May 10, If the employee satisfies the holding period requirements, the company issuing the ISO receives no deduction at either the time of grant or exercise of the ISO.
In addition, based on the Internal Revenue Code the Code , the following requirements must be met in order to be properly considered an ISO:.
If any of the above requirements are not satisfied, then the options are generally treated as nonqualified stock options, which are discussed in further detail below. Nonqualified stock options NSOs do not meet all of the requirements of the Code to be qualified as ISOs. Unlike ISOs, NSOs can be issued to anyone, including employees, consultants, vendors, and members of the board of directors.

From a tax perspective, the recipient generally recognizes ordinary income upon exercise, equal to the excess of the fair market value of the stock at the date of exercise over the exercise price of the option. The company is required to withhold income and employment taxes at the time of exercise and will generally receive a tax deduction equal to the amount of ordinary income recognized by the recipient.
Depending on the terms of the grant, an NSO may also be subject to the penalty provisions in Section A of the Code for deferred compensation.
Incentive Stock Options vs. Nonqualified Stock Options - A General Summary - Lexology
As discussed in this summary, whether an option issued by a company is treated as an NSO or ISO will directly impact the tax consequences upon exercise to the recipient as well as the company. If you are interested in submitting an article to Lexology, please contact Andrew Teague at ateague GlobeBMG.
I particularly like the user-friendly format, which I find highly efficient! Florian Zabel Head of Legal, Asia Pacific Roche Diagnostics. We use cookies to customise content for your subscription and for analytics.

If you continue to browse Lexology, we will assume that you are happy to receive all our cookies. For further information please read our Cookie Policy. Newsfeed Navigator Analytics Track Discover.
Share Facebook Twitter Google Plus Linked In. Follow Please login to follow content.
Register now for your free, tailored, daily legal newsfeed service. Incentive Stock Options vs.
I had a nonstatutory stock option sale reported in box 12 as a V - TurboTax Support
Nonqualified Stock Options - A General Summary Blog GT Israel Law Blog Greenberg Traurig LLP. USA May 26 Introduction When reviewing U.
Incentive Stock Options Subject to certain exceptions as discussed below, an ISO is generally eligible for the following tax benefits: In addition, based on the Internal Revenue Code the Code , the following requirements must be met in order to be properly considered an ISO: Nonqualified Stock Options Nonqualified stock options NSOs do not meet all of the requirements of the Code to be qualified as ISOs.
Conclusion As discussed in this summary, whether an option issued by a company is treated as an NSO or ISO will directly impact the tax consequences upon exercise to the recipient as well as the company.
Non-qualified Stock Options- Theresa Oatman CEPGreenberg Traurig LLP - Aaron R. Katz and Noam Lipshitz.
More from GT Israel Law Blog. Back to Top RSS feeds Contact Submissions About. Testimonials Cookies Disclaimer Privacy policy. Login Register Follow on Twitter Search.